Residual limb pain
Get in touch
There are many potential sources of pain in the residual limb. These include:
- Scars
- Neuromas
- Phantom limb pain
- Folliculitis – inflammation of hair follicles
- Bursas – areas deep inside the residual limb where the soft-tissues rub against the bone and become inflammed.
- Skin cysts and ulcers
- Heterotopic ossifiction resulting in bony prominences
There are different methods of treatment for each source of pain:
Scars
Areas of skin graft (scar) are generally insensate and therefore unlikely to result in much discomfort. However, the surrounding normal skin retains its nerve supply and the scars at the edges of a skin graft are often sensitive. This is particularly true if there are neuromas at the graft edges and/or if the scars become hypertrophic. The surgery to deal with painful scars is considered elsewhere in this website.
Neuromas
Neuromas may require specific surgical intervention using surgical techniques such as RPNI (regenerative peripheral nerve interface) or TMR (targeted muscle reinnervation) surgery. A more complete discussion of these techniques and their potential benefits is detailed via the links.
Phantom Limb Pain
Phantom limb pain may well be relieved by:
- Osseointegration surgery
- TMR surgery
- RPNI surgery
- Mirror therapy
- Augmented reality
In all cases, we believe that the reason for the relief of the phantom pain is the provision of feedback to the central nervous system which allows the baseline sensation to be reset to normal.
Folliculitis
Folliculitis is the result of inflammation of the hair follicles on the residual limb. These may become inflamed and painful due to constant irritation and rubbing in the socket when the hairs are pulled within the silicone liner. The only way to deal with this is to remove the hairs completely. This is harder to achieve than it sounds and requires the amputee to be single-minded in their determination to achieve this aim. Methods which you may wish to consider include:
- Hair removal products (e.g. Nair)
- Waxing to remove hairs
- Laser hair removal
The aim of the treatment is to achieve a smooth and hairless skin surface within the socket. Surgery is not effective in achieving these aims therefore not required.
Skin Cysts
Skin cysts form if skin glands (e.g. sweat glands) become obstructed or if the folliculitis is severe resulting in obstruction of a hair follicle. In a worst-case scenario, patients may develop a condition called hidradenitis suppurativa which is characterised by multiple, painful, discharging cysts and sinuses in the affected skin.
When this happens, the only solution is surgical excision of the cysts and/or areas of affected skin. Therefore, the better solution is to avoid this happening through regular attention to hair removal or by considering an option such as osseointegration to avoid the need for a socket altogether.
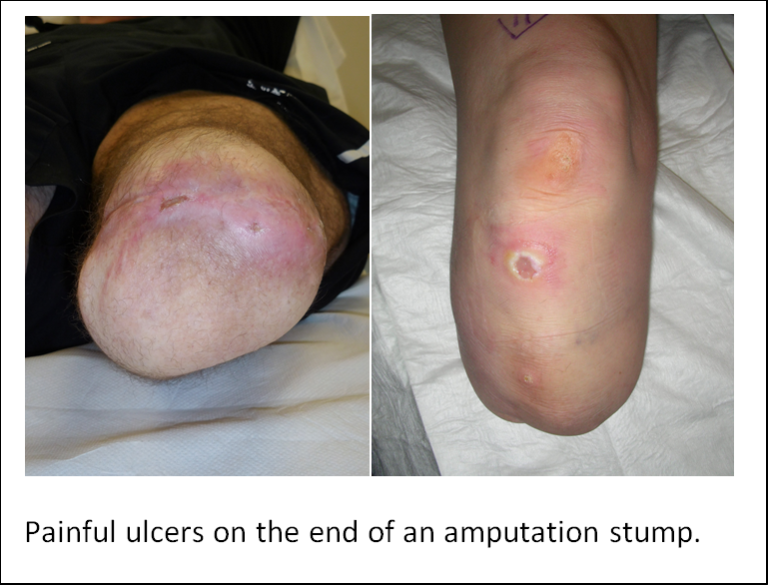
Skin ulcers are of course painful and tend to form wherever the skin is experiencing excessive chaffing, rubbing or pressure inside a socket because the skin of the stump is not intended to be weight-bearing. The skin of the foot is a specialised structure which is designed specifically to be weight-bearing and it is of course absent in a lower limb amputee. Therefore, an ulcer forms when the normal skin is asked to perform a function that it was never designed to do.
At Relimb™, we can excise the ulcer but if the reason that it formed in the first place has not changed (e.g. excessive weight, poorly fitting socket) then it will simply re-form again. The better solution would be to do away with the socket altogether by considering osseointegration to avoid this altogether.
Bursas
Bursas are cavities in the tissues which form where the tissues rub against the residual bone. If the rubbing is excessive, the bursa may become inflamed resulting in pain. When this happens, the solutions are to either excise the bursa or to try and inject it with steroids to reduce the inflammation. The injections are sometimes able to obliterate the bursa cavity.
