Microtia
Get in touch
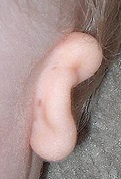
Microtia reconstruction necessitates recreating the ear’s contours with a resilient framework for which the ideal material is the patient’s own rib cartilage. Surgeons who are experienced in sculpting rib cartilage can reliably reproduce the contours of the ear. While there will be a small scar of around 6cm on the chest, the rib is reconstructed during surgery so no deformity results.
The Greek word “microtia” means, in English, “small ear”. The condition occurs in 1 in 6000 babies around the world which means something around 80 children a year are born with the condition in the UK. Mostly, it presents without any other detectable problem, but it can be linked to conditions such as Hemifacial Microsomia, Goldenhar’s Syndrome, Treacher Collins Syndrome and other rarer conditions.
Procedure
In microdot surgery, there are 3 different treatments a patient can opt for:
- No treatment. Some parents could think that the abnormality of the childs ear will have no negative effect on the childs self-esteem therefore no treatment may be needed.
- Prosthetic ears. These can be made for the child and attached to the bone using pins. However if this decision is made it can cause difficulty if the patient wants to opt for ear reconstruction surgery in the future.
- Ear reconstruction surgery – This is a specialised surgery offered by our plastic surgeons
If the patient opts for surgery, two operations are usually necessary: The first stage involves removing the rib cartilage and sculpting a framework from it. The framework is then placed in a skin pocket at the site of the new ear.
In the second operation, performed around six months after the first, the ear framework is released from the pocket, to give it prominence and create the sulcus behind it with symmetry with the other ear being the aim of the surgery.
It is advised not to be tempted or persuaded into surgery before a child is around 8 years of age. Synthetic reconstructions are generally reserved for cases in which rib cartilage cannot be use, for example when it is damaged or calcified. In such cases, a prosthesis can be placed under the skin or can sit outside the skin while being attached to the head with bone anchors. But the gold-standard treatment for a durable, stable ear involves using the patient’s own tissues, and other techniques are advised only when rib cartilage reconstruction is not possible.
